This material is part of the course Practical Introduction to Parallel Programming and meant for educational purposes only.
Background
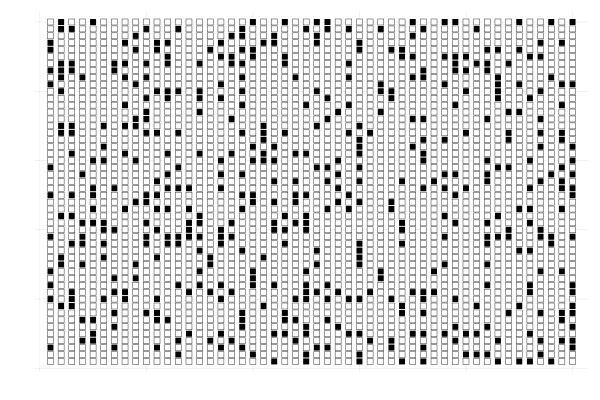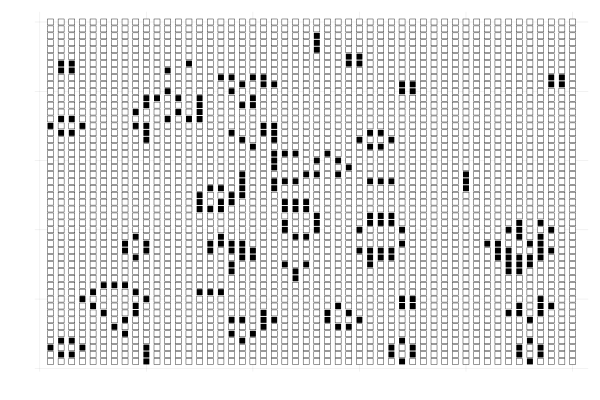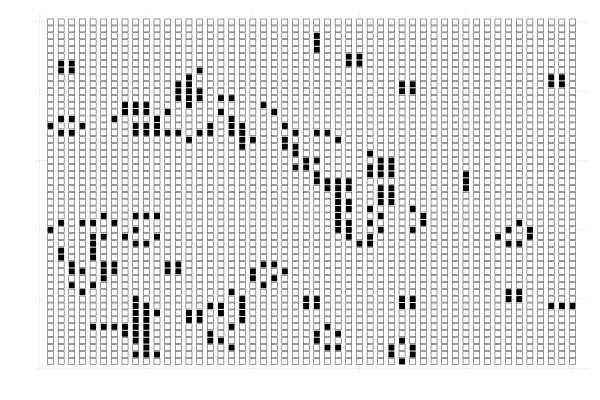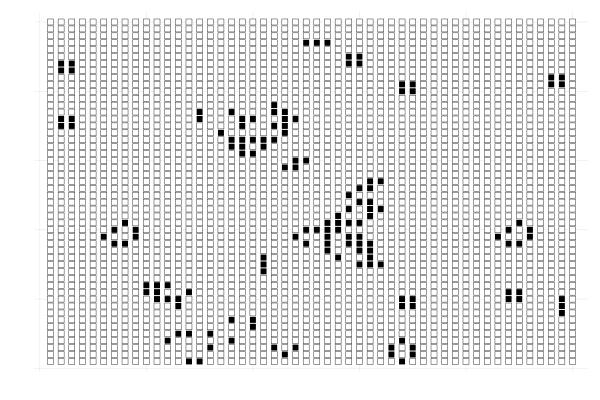
Conway's game of life describes the evolution of a \(m \times n\) grid in which each cell has an associated value that is either zero or one.
The value of a cell in the next time step depends on the values of the neighboring cells in the current time step.
The neighbors of a cell \((i,j)\) are the cells \((i \pm 1, j \pm 1)\).
The initial state of the grid completely determines how the grid evolves in time.
The value of a cell transitions according to the following rules:
- a non-zero cell becomes zero if it has less than two non-zero neighbors;
- a non-zero cell remains non zero if it has two or three non-zero neighbors;
- a non-zero cell becomes zero if it has more than three non-zero neighbors;
- a zero cell becomes non zero if it has exactly three non-zero neighbors.
 INGInious
INGInious