This material is part of the course Practical Introduction to Parallel Programming and meant for educational purposes only.
Background
The area of a circle of radius \(R\) is \(\pi R^2\), the area of a square with side length \(2R\) is \(4R^2\). If the circle is inscribed inside the square then the ratio of both areas is \(\pi/4\).
Monte Carlo method
If we pick \(N\) points at random inside the square and count the number of points that are inside the circle (\(M\)) then we can compute the approximation \(\pi\approx 4M/N\).
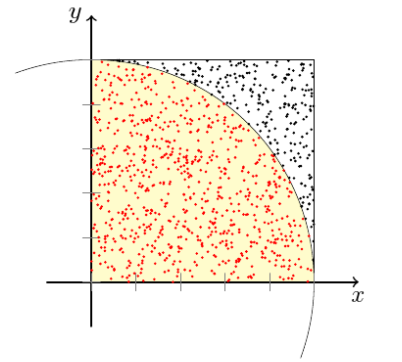
Hints
Use the conf_t data type to obtain the number of iterations \(N\) and the number of threads from the command-line arguments passed to the program.
Call the function parse_args to parse the command line arguments.
Pass the conf object to each thread so that it knows how many iterations it should execute.
Use malloc to allocate an array of thread identifiers in the main thread.
Test your program with the command-line arguments:
"--niter","40000","--nthreads","4".
 INGInious
INGInious